New report on Uganda’s software developers landscape released
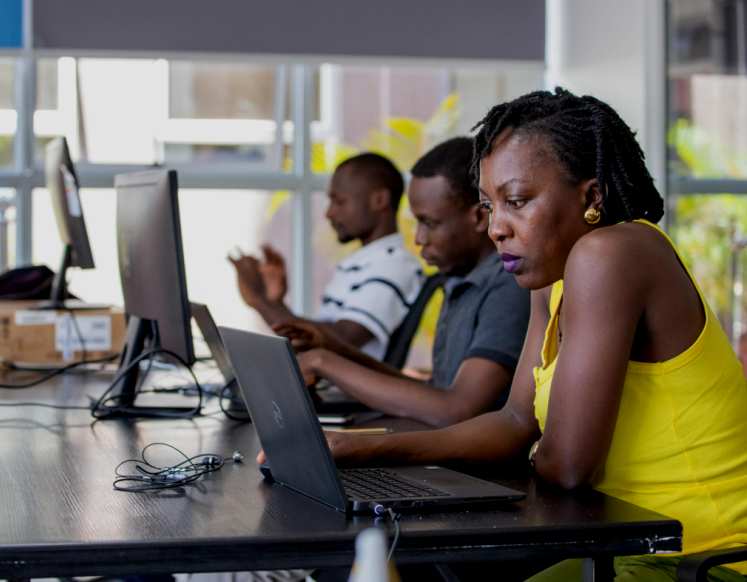 Uganda’s tech industry remains male-dominated with the results from the report showing that only 23.4 pc of them are female.
Uganda’s tech industry remains male-dominated with the results from the report showing that only 23.4 pc of them are female.
Most of the software developers in Uganda are young and concentrated around the central region according to findings from a new report jointly published by The Innovation Village in Kampala and the Mastercard Foundation.
The ‘DevScape’ developer survey report analyzes the current state of the technology start-up landscape in Uganda together with providing options to help harness local talent and nurture it into an expanding pool of capable young developers.
Renita Nabisubi, the Digital Economy Lead at Mastercard Foundation Uganda said during the virtual launch of the report, “The digital space in Uganda is young yet growing fast. Today, digital technology is undoubtedly playing a key role in creating work opportunities for young people by removing geographical barriers. In the rollout of its Young Africa Works in Uganda strategy, the Mastercard Foundation has identified the digital sector amongst its priority sectors in Uganda with the goal of attracting more young people.”
The Innovation Village is a launch pad for leading entrepreneurs and innovators working to solve some of the most pressing challenges using technology. Part of the Mastercard Foundation global outreach programme is to work with entrepreneurs, universities, companies, and funders to translate innovative ideas into large-scale solutions.
Japheth Kawanguzi, Team Lead at The Innovation Village said, “With today’s disruptive environment, we can no longer ignore how technology has grown and infiltrated many economies, including ours. We cannot advance without software developers and information technology expertise. Developers offer us more than websites and applications.”
The DevScape report seeks to understand the number of developers, their demographics, region, gender and age; their engineering journey, coding methods and languages; and levels of education, area of specialization, and experience.
Wilson Kiggundu the Chief Technology Officer at The Innovation Village said 73.4 pc of developers in Uganda are under the age of 30 with 79.5 pc living in the central region of the country. “This implies that Uganda’s developer population is young and has the potential to grow. For this to occur, we require the joint efforts of the technology ecosystem, talent pool of developers, and innovation hubs to mentor and train these young developers,” he said.
A total of 1,288 developers were surveyed, including anyone who builds and creates software and applications. The survey also included software developers, computer programmers, programmers, software coders and software engineers.
Currently, Uganda is experiencing a digital technology evolution. Software development and Innovation Technology (IT) have become influential in affecting how businesses, organizations, and various sectors operate when developing products, improving service delivery, and solving problems affecting consumers.
Kiggundu said Uganda’s tech industry remains male-dominated with the results from the report showing that only 23.4 pc of the developers are female. He said, “While the number of females in the tech space remains low, we are moving in the right direction. The Innovation Village has put a lot of effort to encourage females to become developers and to learn coding through the Women in Tech series and the Code Queen program.”
While 63.1 pc of developers became coders in a professional capacity after attaining technical skills in computing, information technology, and programming, with the evolving nature of the industry and access to the internet, there are various ways one can learn coding. According to the report, 29.9 pc of respondents said they learned how to code from online courses, however majority of developers become full-stack developers, which means they are able to do both front-end and back-end development.
Today, with a large pool of online resources, both free and paid, it is possible for anyone interested in embarking on a software engineering journey to start learning. Kiggundu said, “Other learning avenues for developers in Uganda include boot camps and hackathons. Developer groups also play a role in creating interest and providing a foundation for software engineers.

 Chinese brands strengthen hold on African smart phone market in 2023
Chinese brands strengthen hold on African smart phone market in 2023
 Boeing opens African pathways to space
Boeing opens African pathways to space
 Rolls-Royce basks in expanding African footprint
Rolls-Royce basks in expanding African footprint
 Airlines and airports spent a record USD 45 billion on IT in 2023
Airlines and airports spent a record USD 45 billion on IT in 2023
 Tanzania, Ethiopia join Boeing supported space education initiative
Tanzania, Ethiopia join Boeing supported space education initiative
 KMC projects need for 6000 electric bus drivers in Uganda by 2028
KMC projects need for 6000 electric bus drivers in Uganda by 2028
